In a world where technology is evolving at lightning speed, traditional training methods are being reimagined across every industry—including lifesaving skills like first aid and CPR. From virtual reality simulations to app-based learning platforms, today’s first aid and CPR courses are more accessible, engaging, and effective than ever before.
This transformation is not just a novelty; it’s a necessity. According to the American Heart Association, nearly 70% of cardiac arrests occur at home, and immediate CPR can double or even triple chances of survival. Yet, many people still hesitate to act in emergencies due to a lack of training or confidence. Technology is changing that by making education more available and reducing barriers to learning.
The Rise of Virtual and Augmented Reality
One of the most exciting developments in the training landscape is the use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). These immersive tools allow learners to experience real-life emergency scenarios without real-world risk. Users can practice CPR on a virtual patient, receive instant feedback on their technique, and build muscle memory—all from the comfort of their home or a training facility equipped with VR tools.
AR-enhanced first aid scenarios can overlay digital instructions on physical mannequins, guiding users through each step of the process in real-time. This type of learning is especially valuable in high-stress situations, helping trainees retain information and remain calm under pressure.
Online Learning and Mobile Accessibility
The global shift toward online learning has also impacted how people access first aid and CPR certification. Interactive e-learning modules allow participants to complete the theory portion of their training online, followed by an in-person or blended practical session. This flexible model is especially beneficial for busy professionals, students, and parents who may struggle to attend in-person classes.
Mobile applications further support ongoing learning and emergency response. Apps like PulsePoint and First Aid by the Red Cross offer step-by-step guidance for CPR, wound care, choking, and more. Some even send alerts when someone nearby is experiencing cardiac arrest, enabling trained bystanders to respond before emergency services arrive.
Data-Driven Improvement
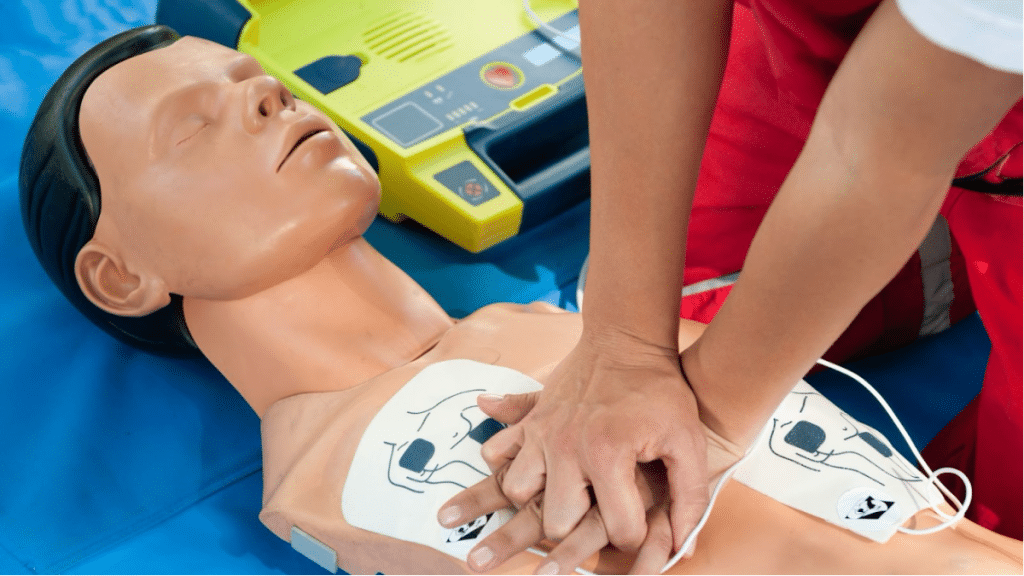
Instructors and organizations are now using data analytics to assess learner performance, track progress, and refine course content. Smart mannequins can measure compression depth, speed, and hand placement during CPR practice, ensuring students meet recommended guidelines. This data-driven approach not only improves skill acquisition but also helps training centers maintain high standards of instruction.
For example, a first aid course provider, like Coast2Coast First Aid, may use this technology to ensure every participant leaves the class with practical, real-world readiness. By leveraging smart feedback tools, these courses are moving beyond rote memorization and into the realm of skill mastery.
Community Preparedness and Accessibility
Technology also plays a critical role in democratizing access to lifesaving education. Rural communities, where access to in-person courses may be limited, can now take advantage of online modules and remote instruction. Language translation tools and subtitles make courses more inclusive, allowing non-native English speakers to learn effectively.
In cities like Oshawa, tech-enabled programs are helping to build stronger, more prepared communities. Enrolling in a first aid and CPR course Oshawa isn’t just about personal development—it’s a commitment to public safety and community resilience.
The Future of Lifesaving Skills
As technology continues to advance, the integration of AI, biometric sensors, and even wearable training aids may soon become standard in CPR and first aid education. These innovations hold the potential to further personalize training, making it more responsive to individual learning styles and needs.
Ultimately, the goal remains the same: to empower more people with the confidence and competence to act in emergencies. With the support of cutting-edge tools and modern training strategies, that goal is now more attainable than ever.