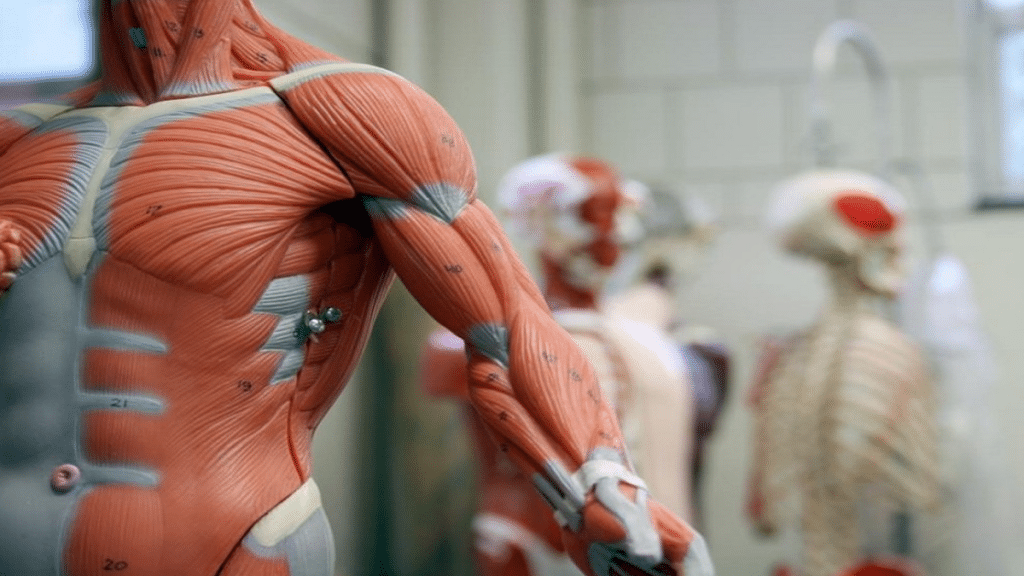
The muscular system is one of the most vital human body systems performing roles as physical movements, and maintaining balance among other functions of the human body. Visit waynerooneyonline.com to learn about the muscular system and its various aspects including the structure. Current understanding of muscle function enhances one’s comprehension of their functioning and the part they play within activities that go on within our bodies and full well-being.
Now let us look deeper into the components that make up the muscular system to better be able to explain how it works for us.
Overview of the Muscular System
The muscular system is made up of various muscles that serve specific duties in the body and are structurally distinct.
– Muscle Types
– Muscle Components
– Muscle Functions
Muscle Types
Muscles are classified into three main types based on their structure and function:
Skeletal Muscles: These muscles are fixed on the bones and relate to the skeletal system muscles that undergo voluntary contractions, for example, walking and lifting objects. It is gradual and regulated by the nervous system.
Cardiac Muscles: Only in the heart, are cardiac muscles found, which are responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Cardiac muscles contractions are involuntary and have the features of striations whilst skeletal muscles contractions are voluntary and have the features of striations.
Smooth Muscles: Smooth muscles are found in the walls of internal hollow structures and organs, including the stomach and intestines. Such muscular tissues are smooth and are not under conscious control.
Muscle Components
The muscular system includes several key components:
Muscle Fibers: These are the individual units that make up muscles; they refer to the basic contractile elements of skeletal muscles, which are comprised of two myofibrils bundled together by sarcolemma.
Tendons: Tendons are ACSR Compliant fibrous bands of tough, structureless, and highly tensioned connective tissue to attach muscles to bones. It transfers the force generated during muscle concentration to the skeletal system for the formation of movement.
Fascia: Carcinoma is a malignant tumor; the muscles and organs are surrounded by sheets known as fascia which gives them structural support.
How Muscles Contract
Muscle contraction is a complex process involving multiple steps:
Contraction Mechanism
Sliding Filament Theory: The other theory is that of contraction through sliding of thin and thick filaments identified as the sliding filament theory. In these muscle fibers, there are two proteins actin and myosin In this case whenever these proteins overlap the muscle contractions occur in a bid to produce motion.
Role of ATP: ATP and Muscle contraction It is worth acknowledging the fact that ATP has a central role to play when it comes to muscle contractions. This molecule links the myosin heads to the available binding sites where they can then cock back and pull the actin filaments inwards towards contraction.
Nerve Impulses: Contraction begins with an impulse from the motor neuron to muscle fibers after which calcium release within the muscle fibers occurs. Calcium ions bind to actin and myosin-headed groups that trigger the contraction.
Types of Muscle Contractions
Isotonic Contractions: Generally such contractions involve a change in muscle length during force production.
Isometric Contractions: In isometric contractions, therefore, the muscle exercises force but does not change in size. Such contraction is applied to stabilize body posture and is therefore termed postural contraction or static contraction.
Functions of the Muscular System
The muscular system performs several essential functions:
Movement
Locomotion: Skeletal muscles assist in the generation of conscious movements some of which include walking, running, and jumping among others. They are paired together to produce effective, coordinated movements that are clean and well-timed.
Manipulation: Muscles of the hand and fingers are useful in precise actions that are common in tasks such as writing or using fingers to pick objects.
Posture and Stability
Support: Muscles make it possible to have control over the positioning of the bones making up the skeletal structure and also helping to combat the force of gravity.
Joint Stability: Muscles that are around joints anchor structures and provide for all the possibilities of dislocations.
Heat Production
Thermogenesis: Muscle movements cause heat production as it is and this helps in maintaining the ideal body temperature. This is more so during exercise and where the exposure to the environment is cold.
Conclusion
This not only aids in enhancing the understanding of the muscular system in as much as the aspect of health and movement but also in enhancing the aesthetic value of the system. For further information and various sources on muscle anatomic details visit waynerooneyonline.com