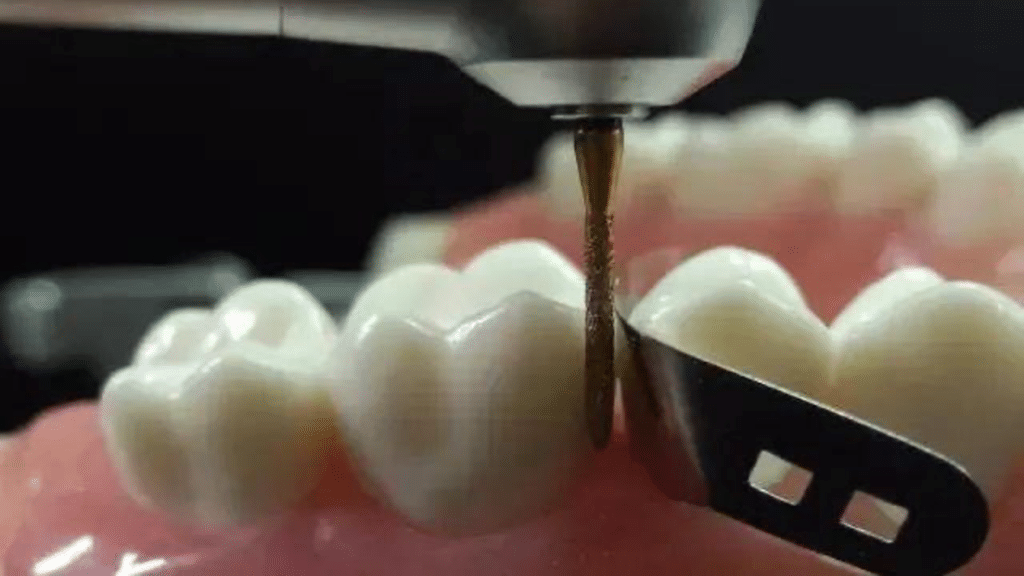
Endodontic bur is one of the most common consumables in dentistry. It is a tiny steel needle featuring a tip and a shank. It is used to create access to the pulp chamber and root canals. But the root canal treatment always comes with different circumstances. Therefore, the small needles have breached numerous branches to cater to the complicated situations.
This guide will bring you through all the basic knowledge of endodontic burs for root canal treatment.
Common Factors to Differentiate Dental Burs
Dental burs can never be a one-size-fits-all solution. They come in many different varieties, each designed for a unique purpose.
Sorted by Grit Size (Color-Coding):
Dental burs are colour-coded based on their grit size, which reflects the particle size and cutting efficiency:
- Black: Super coarse (150μm) – Used for rapid cutting.
- Green: Coarse (125μm) – Effective for initial tooth preparation.
- Blue: Standard (105μm) – Medium grit; commonly used for general cutting.
- Red: Fine (45μm) – Smoothens surfaces after initial cuts.
- Yellow: Extra-fine (25μm) – Used for polishing surfaces.
- White: Ultra-fine (15μm) – For finishing with maximum smoothness.
Coarser burs offer faster cutting but leave rougher surfaces, while finer burs are used for precision finishing and polishing.
Shapes
- Ball Shape (B Series): Ideal for cavity preparation and creating rounded contours.
- BC: With diamond coating.
- BR: Without diamond coating.
- Tapered Shape (T Series): Commonly used for crown preparation.
- TF: Flat-end taper for shoulder preparation.
- TC: Pointed-end taper for axial wall shaping.
- TR: Round-end taper for ceramic crown shoulder preparation.
- Straight Shape (S Series): Used for cavity and box preparations.
- SF: Flat-end straight.
- SR: Round-end straight.
- SO: Pointed-end with 45-degree tip.
- Flame Shape (FO): Ideal for occlusal surface or lingual anterior preparation.
- Inverted Cone (SI/DI): Used for undercutting and cavity shaping.
- Disc Shape (WR): Suitable for incisal edge adjustments.
Length
- S (Short Shank): Short shank.
- SS (Ultra-Short Shank): Ultra-short shank.
- C (Coarse): Coarse.
- F (Fine): Fine.
- EF (Extra-Fine): Extra-fine.
- L (Extended Length): Extended length.
Material
- Diamond Burs: Made with natural or synthetic diamond grit; ideal for cutting hard tissues like enamel and ceramics.

- Carbide Burs: Tungsten carbide burs offer durability and precision for metal and composite cutting.

- Disposable Burs: Designed for single use to ensure sharpness and infection control.
- Reusable Burs: Suitable for repeated sterilisation and long-term use.
Rotation
- High-Speed Burs (16,000-45,000 RPM): Used with turbine handpieces for fast and efficient cutting.
- Low-Speed Burs (under 16,000 RPM): Used for polishing, finishing, and adjustments.
How to Read the ISO Number of Dental Burs:
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides a standardised system for identifying dental burs. Each compliant bur features an ISO code, which consists of five groups of numbers, each representing specific characteristics.
While manufacturers may have their unique codes, ISO codes are universally used for clarity, especially the third and fifth groups, which specify bur shape and diameter.
Example: 806-314-233-534-012
- First Group (3 digits): Material type:
- 806: Diamond burs.
- 500: Tungsten carbide burs.
- Second Group (3 digits): Shank type and length:
- The first digit indicates handpiece compatibility:
- 1: Straight handpiece.
- 2: Contra-angle handpiece.
- 3: Turbine handpiece.
- The final digit specifies length:
- 4: Standard.
- Larger or smaller numbers denote extra-short, long, or extra-long shanks.
- Third Group (6 digits): Head shape and features:
- 233: Represents bur head shape (e.g., inverted cone).
- 534: Denotes specific cutting features, such as fine or wide blades.
- Fifth Group (3 digits): Maximum diameter of the bur head:
- 012: Indicates a 1.2mm maximum head diameter.
- The first digit indicates handpiece compatibility:
Factors to Consider When Choosing Endodontic Burs
Making choices among all the shapes, sizes, and grits can be the basic. The basic features shape the functions like:
- Ball-shaped Diamond Bur (Blue band, 1.0mm diameter): Used for initial shoulder margin positioning. Reason: Veneer shoulder width ranges between 0.3 to 0.5mm, and the 1.0mm diameter ball-shaped bur ensures stable edge positioning.
- Depth-Determining Bur (for Labial Surface): Specialized or customised depth-control burs. Selection depends on the veneer material and final position. Significance: Determines the reduction depth under the guidance of diagnostic wax-up and silicone guides.
- Initial Labial Preparation Bur: This can be the same as the customised depth-determining bur, performing both depth marking and initial grinding. (Blue or green band, round-end tapered bur, max diameter 1.6mm). Purpose: Removes required tooth structure on the labial surface.
- Labial Polishing Bur: (Red or yellow band, round-end tapered bur): Matches the initial labial preparation bur in size and shape. Purpose: Polishes the prepared surface after initial grinding.
- Proximal Opening Bur: (Pointed or round-end straight bur, max diameter 1.2mm): Used to create spacing between adjacent teeth to avoid damage during preparation.
- Shoulder Polishing Carbide Bur: (Round-end tapered or round-end straight bur, max diameter 1.6mm): Shapes and polishes a shallow concave shoulder margin.
Durability And Reusability
Now, let’s discuss durability and reusability. Some burs are designed for single use, making them ideal for procedures that require pristine, new tools each time. But for those who need something more long-lasting, reusable burs are a cost-effective and environmentally friendly option. Just make sure they’re sterilised properly!
Compatibility and Cost-Effectiveness
Compatibility with your equipment is the most important factor. Regarding cost-effectiveness, a balance must be maintained between quality and price. It’s not worth splurging on high-end burs, but neither do you want to compromise the quality of tools that’ll make or break your procedure.

Dental Perfect Dental Burs
Recently, Dental Perfect has rolled out a series of endo burs (diamond and carbide burs) that feature top-notch quality.
Dental Perfect premium-grade diamond burs are made from imported natural diamond powder; the material undergoes rigorous processes like impurity removal, demagnetisation, rounding, and purification to ensure superior quality. Each burs are crafted precisely for efficient root canal treatment preparation.
The carbide burs are engineered for unmatched strength, durability, and cutting efficiency. With hardness 2-3 times that of standard steel and up to 6 times harder than enamel, these burs excel in tough dental procedures while offering extended lifespans 4-5 times longer than diamond burs. The perfect concentricity ensures stable, vibration-free performance for enhanced patient comfort and protection of handpiece bearings.
As the world’s leading endodontic instrument and equipment provider, Dental Perfect has been committed to providing quality and innovative endo instruments and equipment to enhance treatment quality and efficiency.