Feeling restless at night while your mind races with worries? You’re not alone. Anxiety can deeply influence your sleep, creating a cycle that seems hard to break. Poor sleep doesn’t merely leave you tired; it can exacerbate your anxiety, affecting your overall mental well-being.
In this article, we’ll explore how anxiety affects your sleep patterns and provide practical strategies to manage anxiety and improve sleep quality. Let’s dive into understanding this connection and discovering ways to achieve more restful nights and peaceful days.
The Interplay Between Anxiety and Sleep Disorders
Chronic anxiety is a major contributor to the onset and maintenance of sleep disorders, such as insomnia. Anxiety can cause frequent awakenings and fragmented sleep, reducing your overall sleep quality.
Chronic Anxiety and Insomnia
When you’re constantly worried and stressed, it becomes difficult for your mind and body to relax, making it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night. This disruption in your sleep cycle can lead to daytime fatigue, irritability, and decreased productivity.
Anxiety-Induced Sleep Fragmentation
You may find yourself waking up multiple times during the night, often with racing thoughts or feelings of unease. This pattern of interrupted sleep prevents you from getting the deep, restorative sleep your body needs to function optimally.
Effects of Sleeping Pills on Anxiety and Sleep
While sleeping pills may provide temporary relief for anxiety-related sleep problems, they can lead to dependency, tolerance, rebound insomnia, and various side effects when used frequently or for an extended period.
The Prevalence of Sleeping Pill Use
Sleeping pills are commonly prescribed for individuals struggling with insomnia and anxiety-related sleep disturbances. According to a study by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 4% of U.S. adults aged 20 and over reported using prescription sleep aids in the past month.
Yet, frequent use of sleeping pills can result in adverse effects and addiction.
The Path to Sleeping Pill Addiction
The path to sleeping pill addiction often starts innocently, with occasional use to manage anxiety-related sleep problems. As you experience relief from the medication, you may be tempted to use them more frequently, believing they are the only solution.
Your body quickly develops a tolerance to the medication, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect. This tolerance can develop within weeks, leading you to take more pills than prescribed or for longer periods.
As tolerance increases, individuals may find themselves depending on sleeping pills every night. You might struggle to sleep without them, leading to psychological dependence. This dependence is reinforced by the fear of sleeplessness, creating a vicious cycle of anxiety and pill use.
When attempting to stop, you may experience withdrawal symptoms such as rebound insomnia, anxiety, and irritability. These distressing symptoms can make you believe you cannot cope without the medication, perpetuating the addiction cycle.
The ease with which one can fall into sleeping pills addiction is concerning, as many people are not realizing the potential dangers when they first start using the medication. They may believe that because a doctor prescribed the pills, they are safe to use long-term. However, the risk of developing a sleeping pill addiction is real and can have severe consequences for your mental and physical health.
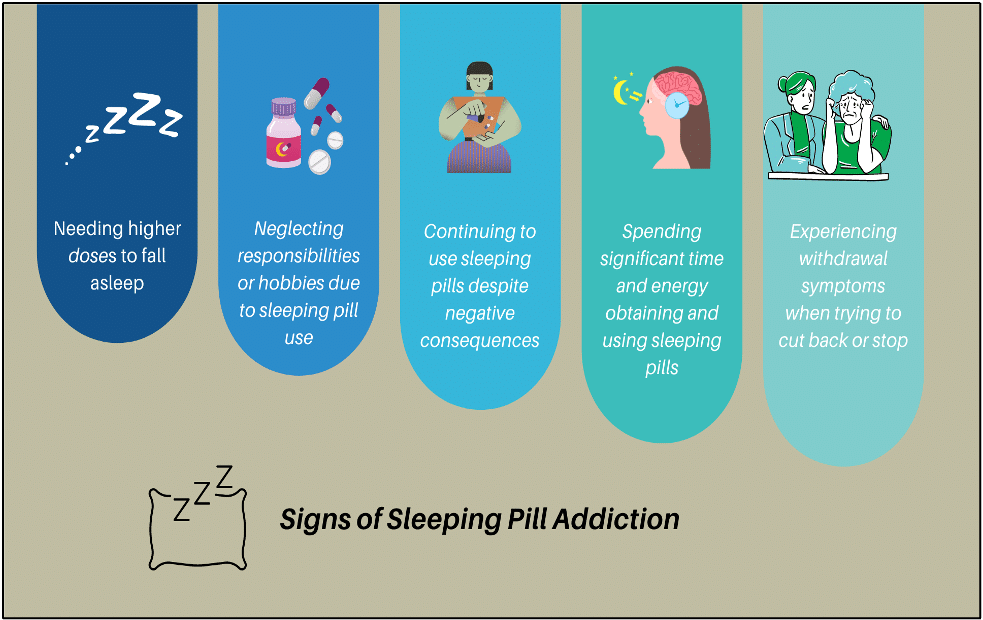
If you recognize these signs in yourself or a loved one, it is crucial to seek professional help to overcome sleeping pill addiction. A healthcare provider can work with you to develop a safe and effective plan to taper off the medication and address the underlying anxiety and sleep issues through therapy and alternative coping strategies.
Physiological Mechanisms Linking Anxiety and Sleep Disruption
Anxiety triggers the release of stress hormones and leads to a state of hyperarousal, both of which can significantly interfere with your ability to fall asleep and maintain a stable sleep cycle.
Stress Hormones and Sleep
When you’re anxious, your body releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. Elevated levels of these hormones can interfere with your ability to fall asleep and maintain a stable sleep cycle.
Hyperarousal and Sleep Disturbances
Hyperarousal is a common feature of anxiety disorders, characterized by a racing heart, rapid breathing, and a constant feeling of being “on edge.” This heightened state of arousal makes it difficult for you to relax and unwind, which is essential for falling asleep.
Psychological Impact of Sleep Deprivation Due to Anxiety
Anxiety-related sleep deprivation can take a significant toll on your cognitive functions and emotional well-being, creating a vicious cycle where anxiety disrupts your sleep, and poor sleep, in turn, worsens your anxiety.
Cognitive Impairment
You may find it harder to concentrate, make decisions, and retain information. This can affect your performance at work or school and leave you feeling frustrated and overwhelmed.
Emotional Dysregulation
When you’re sleep-deprived, you’re more likely to experience mood swings, irritability, and a decreased ability to cope with stress. This can create a vicious cycle, where anxiety disrupts your sleep, and poor sleep, in turn, worsens your anxiety.
Anxiety Disorders and Specific Sleep Issues
Different anxiety disorders, such as Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), can lead to specific sleep problems that can significantly impact your overall mental health and well-being.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and Sleep
If you have GAD, you may experience difficulty falling asleep due to racing thoughts and worries, frequent night awakenings, and restless, non-restorative sleep. These sleep disturbances can leave you feeling exhausted and less equipped to manage your anxiety symptoms during the day.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and Nightmares
If you have PTSD, you may experience frequent nightmares related to the traumatic event, which can cause sleep disturbances and heighten anxiety levels. The fear of having these nightmares can also lead to sleep avoidance, further compounding the problem.
Strategies for Managing Anxiety to Improve Sleep
There are various effective strategies for managing anxiety and improving sleep, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) and mindfulness and relaxation techniques.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
CBT-I focuses on identifying and changing the thoughts and behaviors that contribute to sleep problems. By learning relaxation techniques, restructuring negative thoughts about sleep, and establishing a consistent sleep schedule, you can significantly improve your sleep quality and reduce anxiety symptoms.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and yoga, into your daily routine can help you manage anxiety and enhance sleep quality.
These techniques help calm the mind, reduce stress, and foster a sense of inner peace, facilitating easier sleep initiation and maintenance throughout the night.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Anxiety and Promote Better Sleep
Making lifestyle modifications, such as practicing good sleep hygiene and maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise routine, can play a crucial role in reducing anxiety and promoting better sleep.
Sleep Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good sleep hygiene is crucial for mitigating the effects of anxiety on sleep. Some practical tips include sticking to a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, ensuring your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool, avoiding screens at least an hour before bed, and limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, especially in the evening.
Diet and Exercise
A balanced diet rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, and regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can help reduce stress and improve sleep quality. Remember, consistency is crucial for realizing the benefits of a healthy diet and exercise regimen.
Wrap Up
Anxiety and sleep disturbances are closely intertwined, each exacerbating the other and leading to a host of negative consequences for your mental and physical well-being. By understanding the mechanisms behind this relationship and implementing various strategies to manage your anxiety and improve your sleep, you can break the cycle and reclaim your quality of life.
Remember, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. It may take some trial and error to find the combination of strategies that work best for you. Be patient with yourself and don’t hesitate to seek professional help if needed.
FAQs
1. Can anxiety cause sleep problems?
Yes, anxiety can disrupt sleep, causing trouble falling asleep and frequent nighttime awakenings.
2. How does poor sleep affect mental well-being?
Insufficient sleep can worsen anxiety and depression, creating a cycle of increasing emotional distress and sleep issues.
3. What are effective ways to manage anxiety-related sleep issues?
Using relaxation techniques and adhering to a regular sleep schedule are effective strategies for managing anxiety-induced sleep disturbances.

