
A Distributed photovoltaic (PV) system is a solar-based electric power system. It is called “distributed” because it is installed close to the consumption place. It offers a direct source of clean and eco-friendly electricity, which provides energy independence, free electricity, and reduced transmission losses. Therefore, let’s dive deep into the core of distributed PV systems and discuss their working principle, benefits, and other details.
How Do Distributed PV Systems Work
To better understand the working principle of distributed PV systems, it is important to first clarify the basics of the photovoltaic process.
Basics of Photovoltaic Process
PV cells are key components of distributed PV systems and are composed of different semiconductor materials. When the semiconductor gets exposed to solar energy, it harnesses the light’s energy and transfers it to its electrons (negatively charged particles). This excess energy makes the electrons flow and generates electric current. The electric direct current (DC) is extracted via conductive metal contacts to utilize the generated electricity.
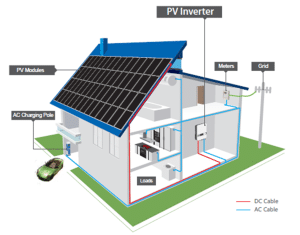
Components of a Distributed PV System
The main components of a distributed PV system include:
- Photovoltaic modules
- Module mounting structure
- Battery bank (stores the generated DC electricity in batteries)
- Solar inverter (On grid inverter or Hybrid inverter)
- Combiner box ( with fuses and circuit breakers for system safety and proper operation)
- Cable and accessories
All the above components make up a complete distributed PV system.
Configuration of a Distributed PV System
The configuration of a typical distributed PV system is as follows:
- An array of PV panels is installed on the rooftop using proper mounting structures. The panels are placed in the right orientation/tilt angle for maximum sunlight exposure. This configuration generally depends on geographical location and local weather factors.
- The electricity generated from PV panels is directed to a solar inverter. In the case of an on-grid inverter, this device converts the direct current (DC) power generated by the panels into alternating current (AC) power. This AC power can then be utilized within the home or exported into the grid for compensation. Alternatively, with a hybrid inverter, besides converting DC to AC, it also facilitates additional functionalities. In addition to supporting household electricity needs and exporting surplus power to the grid, a hybrid inverter can charge a battery bank for backup purposes.
This way, a distributed PV system is configured to generate and supply electricity from solar energy. In addition, based on regional policies, a distributed PV system can be grid-tied, allowing excess electricity to be sold to the grid for monetary compensation or credited towards future electricity consumption.
Benefits of Distributed PV Systems
The growing popularity of distributed PV systems is linked to their diverse range of benefits. Some of the key ones are as follows:
1. Utilization of Solar Energy
Distributed PV systems utilize solar energy, a freely available and abundant renewable energy source. Individuals can harness solar energy through PV panels and generate their own electricity.
2. Grid Reliability and Energy Independence
Distributed PV systems enhance grid reliability by reducing the burden on the grid infrastructure. By generating electricity locally, users gain a degree of energy independence, meeting their essential power needs autonomously and even contributing excess energy back to the grid.
3. Economic Advantages
As mentioned earlier, a distributed PV system is installed closer to the consumption point, such as the house rooftop. This helps reduce dependence on costly grid supply and have free access to electricity. Secondly, it reduces the load on the grid supply, which means less costly energy prices.
4. Environmental Impact
Crucially, distributed PV systems generate no toxic greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil-fuel generation. These systems mitigate harmful environmental impacts by harnessing clean solar energy, promoting a greener and more sustainable energy ecosystem.
How to Choose the Right Distributed PV System for Your Needs
There are different factors to consider when choosing the right distributed PV system. From this perspective, below are some important factors to consider:
1. Energy Consumption Requirements
The first thing to consider is to assess your energy consumption requirements. You have to calculate the total energy consumption of all loads you want to power through the distributed PV system.
For that, calculate the total watt-hours per day of all the appliances and sum up. Afterward, multiply the total watt-hours by the system energy loss factor (a general estimate of 1.3) to get the estimated watt-hours capacity system you should install.
2. Site Assessment
Next, you should conduct a proper site assessment to access the available space for the PV module, tilt angle, and shading complications. In addition, you should also consider the weather conditions and other obstructions that need to be tackled while installing a distributed PV system.
3. Cost-benefit Analysis
Lastly, perform a proper cost-benefit analysis. Estimate the initial installation cost that involves purchasing components and installing the whole system. Afterward, evaluate the financial savings on the electricity bills. You should also consider the government-backed financial incentives you can grab with a distributed PV system. You can estimate your long-term economic benefits with a distributed PV system based on all these calculations.
Conclusion
Distributed PV systems are the need of the hour, considering climate change and higher grid supply costs. It provides solar-based free and eco-friendly electricity and supports the grid supply through net metering. Therefore, it’s time to install a distributed PV system at your home/corporation and leverage its benefits for years to come.
