The past year has marked a significant shift in the landscape of wage and hour regulations across the United States. Federal legislative changes coupled with adjustments at the state level have reshaped the rights and protections afforded to employees nationwide.
As an employee, understanding these updates and their implications is crucial for ensuring fair compensation and compliance with the latest minimum wage updates in 2024.
Understanding Your Rights Under the New Regulations
Overtime Eligibility and Higher Minimum Wages
One of the key changes in wage and hour regulations involves revised overtime eligibility criteria. The Department of Labor (DOL) has updated the thresholds for employees to qualify for overtime pay, potentially impacting a substantial portion of the workforce. Additionally, over 20 states have increased their minimum wage laws, with Washington State and Washington, D.C., leading the pack with the highest minimum wages in the nation.
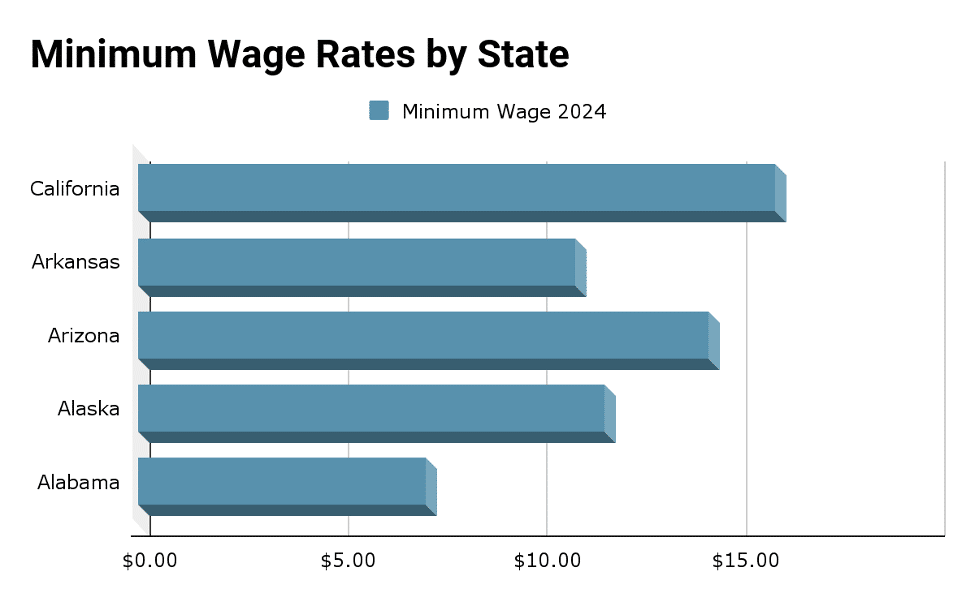
Note: This table provides a snapshot of the top 5 states with the highest minimum wage rates as of 2024. Rates are subject to change, and it’s recommended to consult official state resources for the most up-to-date information.
Protections for Remote and Gig Workers
The evolving regulations have also addressed the unique challenges faced by remote and gig economy workers. With the rise of flexible work arrangements, new provisions aim to ensure equitable treatment and wage law compliance for these non-traditional employment models. This includes clarifications on overtime eligibility, break periods, and other essential worker rights.
For instance, let’s take Los Angeles as an example to illustrate this. The minimum wage in Los Angeles has been gradually increasing and reached $16.04 per hour for employers with 26 or more employees as of July 2022. Employees in Los Angeles may need to consult with a wage and hour attorney Los Angeles to ensure they’re getting paid the right minimum wage and overtime based on the city’s specific laws and the updated federal regulations.
The updated regulations have made strides in extending protections to remote and gig economy workers, who often face unique challenges in areas like overtime eligibility and break periods due to their non-traditional work arrangements.
Comparison With Previous Regulations
To better understand the extent of these changes, it’s important to compare the previous and current wage and hour regulations. The key differences include:
Minimum Wage Adjustments
The federal minimum wage remained stagnant at $7.25 per hour from 2009 until 2023 when it was increased to $13.00 per hour. However, many states had already implemented higher minimum wages, with some exceeding the new federal rate. For example, in 2024, Washington state has the highest minimum wage at $15.74 per hour.
Overtime Eligibility Criteria
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) has significantly increased the salary threshold for overtime pay exemption. Previously set at $455 per week in 2004, the threshold rose to $684 per week in 2020 and further increased to $132,964 per year in 2024. This change has expanded overtime pay eligibility to a larger portion of the workforce.
Pay Transparency Laws
Several states have implemented pay transparency laws, requiring employers to disclose pay ranges in job postings and provide current employees with information about their pay scale upon request. These measures aim to promote pay equity and transparency in the workplace.
Gig Economy Regulations
The rise of the gig economy has prompted new regulations, such as California’s AB5 bill, which reclassified many independent contractors as employees, entitling them to minimum wage and benefits. This shift aims to extend labor protections to non-traditional work arrangements.
State-Specific Adjustments
In addition to federal changes, many states have implemented their own wage and hour regulations, further enhancing employee protections. Some states have set higher minimum wages, while others have introduced industry-specific regulations, such as those targeting the fast food and healthcare sectors.
These comparisons highlight the significant strides made in safeguarding employee rights and promoting fair compensation practices across the nation. However, it’s crucial to stay informed about ongoing changes and ensure compliance with the latest regulations at both the federal and state levels.
Impact on Employment Contracts: What to Watch For
As wage and hour regulations change, it’s essential to review your employment contract to ensure it aligns with the new laws. Employees may need to ensure that clauses related to compensation, overtime provisions, and other terms are updated to reflect the latest requirements. Legal precedents support contract adjustments due to regulatory changes, but employees should remain vigilant and take steps if their current contracts do not comply.
Compliance and Enforcement: Your Rights and Options
The DOL plays a pivotal role in enforcing wage and hour regulations, and employers face penalties for non-compliance. If you suspect your employer is violating the new laws, you have the right to report these violations through the appropriate channels. Understanding the process for reporting is crucial for protecting your interests.
Proactive Strategies to Adapt to New Wage and Hour Laws
Staying informed about further changes in wage and hour regulations is essential. Leverage tools and resources, such as government websites and industry publications, to track updates relevant to your state and industry. Additionally, consider negotiating adjustments to your employment terms to ensure they align with the evolving laws.
Long-Term Impacts on Career Progression
The shifts in wage and hour regulations may influence career paths and progression in various industries. As compensation structures and job responsibilities evolve, it’s essential to prepare for potential changes and opportunities. Proactively assessing how these legal updates might impact your long-term career goals can help you make informed decisions and position yourself for success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What should I do if my employer has not updated our contracts to reflect the new wage and hour laws?
If your employer has not updated your employment contract to align with the latest wage and hour regulations, the first step is to initiate a conversation with HR or management. Clearly communicate your understanding of the new laws and request that the necessary changes be made to your contract. If satisfactory adjustments are not made, you may need to explore legal options or consult with an employment attorney for guidance.
2. How can I keep up with both federal and state changes to wage and hour regulations?
To stay informed about changes to wage and hour regulations at both the federal and state levels, leverage the following resources:
- Subscribe to updates from the Department of Labor (DOL) and your state’s labor department websites.
- Follow reputable legal publications and industry associations for real-time news and analysis.
- Engage with professional networks and industry groups to share insights and best practices.
3. Are there specific protections or provisions for part-time and contract workers under the new regulations?
Yes, the updated wage and hour regulations include inclusive clauses and protections for non-full-time employees, such as part-time workers and contractors. These provisions aim to ensure equitable treatment and compliance with minimum wage laws, overtime eligibility, and other labor standards, regardless of employment status. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with these specific provisions to understand your rights as a part-time or contract worker.
Conclusion
Stay informed about wage and hour regulations to protect your rights at work. Review contracts, report violations, and seek legal advice if needed. These changes aim to ensure fair compensation. Adapt to them for your career success.
Stay vigilant, stay informed, and take action to ensure your rights under the new wage and hour regulations are upheld. Your financial well-being and professional growth depend on it.

