In the realm of manufacturing and fabrication, precision cutting is a critical process that can make or break a product’s quality. Two of the most prominent technologies in this field are CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines and laser cutters. This article aims to dissect these technologies, compare their capabilities, and guide you through the decision-making process when choosing CNC vs laser cutters.
Understanding CNC Machines
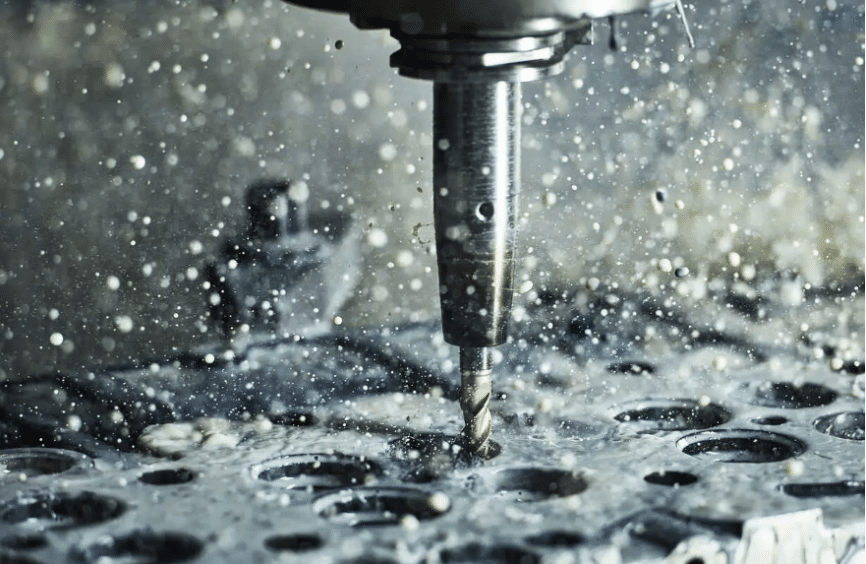
The core of CNC technology is the ability to translate complex designs into a series of numerical commands. This process begins with a design file, which is then converted into G-code—a series of instructions that guide the machine’s movements. The G-code dictates the exact path the cutting tool must follow, the depth of each cut, and the speed at which the tool operates. This level of control allows for the creation of parts with high dimensional accuracy and surface finish quality.
CNC machines perform three-dimensional operations, such as milling and drilling, making them indispensable for producing intricate parts with complex geometries.
Common Materials
The versatility of CNC machines is evident in the range of materials they can process. Here are some of the most common materials worked with by CNC machines:
- Wood: Ideal for woodworking, CNC machines can create detailed furniture, sculptures, and architectural models.
- Plastics: Used in prototyping and manufacturing of various plastic products due to its ease of cutting and shaping.
- Aluminum: A popular choice in the aerospace and automotive industries for its lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio.
- Steel: Employed for heavy-duty applications where high strength and durability are required.
Advantages
The advantages of CNC machines are numerous and contribute significantly to their widespread use in manufacturing:
- Efficiency: CNC machines can operate continuously, producing parts at a high rate with minimal human intervention.
- Precision: The computer-controlled nature of CNC machines ensures that each part produced is identical to the last, reducing variability and ensuring quality control.
- Complexity: They can handle complex designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with manual cutting methods.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in a CNC machine can be high, the reduced labor costs and increased production efficiency can lead to significant savings over time. In addition, choosing cost-effective CNC machining services is also a good choice.
Introduction to Laser Cutters
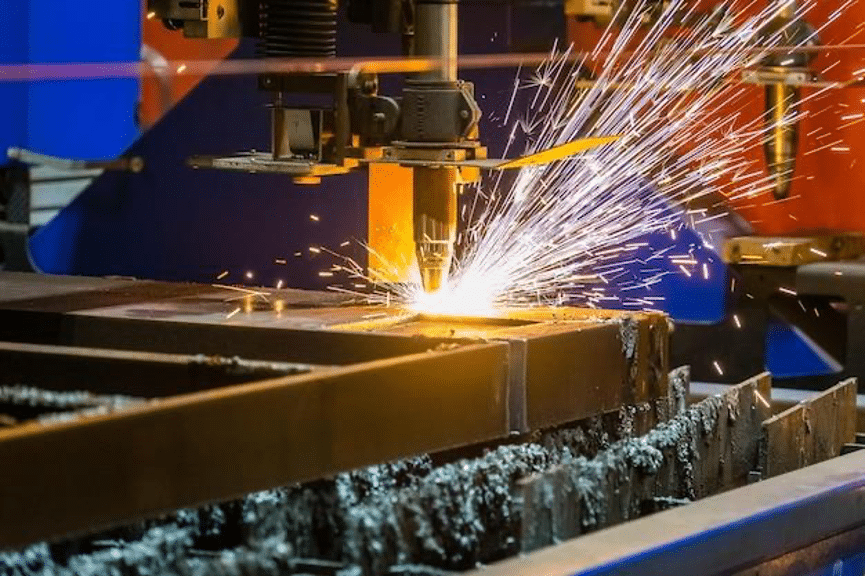
Laser cutting is a thermal cutting process that uses the intense heat generated by a laser beam to separate materials. The process involves directing a laser beam, which is focused by a lens, onto the surface of the material. The material at the point of the laser impact melts, burns, or vaporizes and is then removed by a gas jet, leaving a clean edge behind.
The laser beam can be focused to a very fine point, allowing for the creation of very detailed and intricate designs. Additionally, since the laser does not come into physical contact with the material, there is no tool wear, which can lead to longer machine life and less downtime for maintenance.
Types of Lasers
Different laser types are suited to different materials and applications:
- CO2 Lasers: These are commonly used for cutting non-metallic materials such as wood, acrylic, and textiles. CO2 lasers are known for their ability to produce high-quality cuts with minimal heat-affected zones.
- Fiber Lasers: They are more suitable for cutting metals and some types of plastics. Fiber lasers offer higher energy efficiency and can achieve higher cutting speeds compared to CO2 lasers.
Advantages
Laser cutting offers several distinct advantages that make it a popular choice for many applications:
- Speed: Laser cutters can achieve high cutting speeds, which is particularly beneficial for high-volume production.
- Material Thickness: They can cut through a wide range of material thicknesses, from thin sheets to thicker plates, depending on the power of the laser.
- Edge Quality: The edges produced by laser cutting are often smooth and clean, reducing the need for post-processing such as grinding or polishing.
- Flexibility: Laser cutters can quickly switch between different designs without the need for changing tools or fixtures, making them highly adaptable to changing production demands.
Key Differences Between CNC and Laser Cutters
When it comes to choosing between a CNC machine and a laser cutter, several factors come into play.
- Cutting Speed: Laser cutters generally offer faster cutting speeds, especially for intricate designs and thinner materials.
- Precision and Accuracy: Both technologies are precise, but CNC machines may have an edge in terms of repeatability and the ability to handle thicker materials.
- Material Versatility: CNC machines can cut a wider variety of materials, including thicker and more diverse types, whereas laser cutters excel with thinner, more delicate materials.
- Operating Costs: The cost of operation can vary widely depending on the specific model, maintenance requirements, and the cost of consumables like the laser or cutting tools.
- Safety Considerations: Both technologies require safety precautions, but laser cutters present unique hazards due to the high-energy light they emit, necessitating specific safety measures.
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between a CNC machine and a laser cutter depends on the specific needs of your project. If you require versatility in material types and thickness, a CNC machine may be the better choice. However, for speed and precision in cutting thinner materials, especially with complex designs, a laser cutter could be more suitable.
When considering these options, it’s also important to take into account the operating costs, safety requirements, and the skill level needed to operate the machinery. For those in search of high-quality CNC machining services, HordRT offers a comprehensive range of solutions tailored to meet the precise needs of various projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which is better? Laser cutter or CNC?
The choice between a laser cutter and a CNC machine depends on your specific needs. If you require versatility in material types and thicknesses, a CNC machine is often the better choice due to its ability to handle a wide range of materials, including thicker and more diverse types.
On the other hand, if you prioritize speed and precision for cutting thinner materials with complex designs, a laser cutter may be more suitable. Laser cutters also offer the advantage of not physically contacting the material, which can result in less wear and a smoother edge finish.
2. What is the disadvantage of a laser cutter?
While laser cutters offer speed and precision, they do have some disadvantages. One significant limitation is that they cannot cut certain materials, such as glass or mirrored surfaces, without causing damage to the laser itself. Additionally, laser cutting can be more expensive to operate due to the cost of electricity and the need for specialized consumables like reflective mirrors and focusing lenses. Also, the capital cost for a laser cutting system can be higher compared to an entry-level CNC machine.
3. What materials cannot be cut with a laser cutter?
Laser cutters have difficulty cutting materials that are reflective or have a high thermal conductivity, such as:
- Mirrored Surfaces: The reflective properties can damage the laser.
- Glass: Similar to mirrored surfaces, the reflective nature of glass can cause issues with laser cutting.
- Thick Metals: While some laser cutters can cut metals, they are generally more effective on thinner sheets. Very thick metals may require more powerful lasers, which can be costly.
- PVC and Certain Plastics: These materials can release toxic fumes when cut with a laser, making them unsuitable for this process.
4. How fast is CNC compared to laser?
The cutting speed comparison between CNC and laser cutters can vary based on the material and complexity of the design. Generally, laser cutters can achieve faster cutting speeds, particularly for intricate designs and thinner materials. However, CNC machines are highly efficient for cutting thicker materials and can perform more complex three-dimensional operations. For example, a laser cutter may cut a simple design in a thin sheet of acrylic quickly, while a CNC router would be faster for a detailed part in a dense material like hardwood or thick aluminum.


