The popularity of electric vehicles is not surprising. This convenient and economical mode of transportation offers benefits to both drivers and the environment. Their user base is gradually expanding as options increase and driving ranges improve. However, with the growth of EV ownership comes the need for expanded charging infrastructure. Both individual car owners and public locations need easy access to reliable, best EV charging station solutions. Below are the answers to frequently asked common questions about EV charging. These will help you select the best charging station for your needs.
What is an EV Charger?
An EV charger is a power supply device that provides electricity to the EV batteries. Chargers exist in various designs to accommodate different needs – from slower residential units to faster public infrastructure. Home chargers are usually wall-mounted units that plug into standard electrical outlets to enable Level 1 or Level 2 charging rates. Public fast chargers are floor-standing units capable of Level 3 DC fast charging in minutes. Both connect to the vehicle using standardized plugs that fit the EV’s charge port.
EV chargers work by converting the type of power they receive into the direct current needed by the battery. At home, the best EV charging station takes standard alternating current (AC) from an outlet and converts it to DC through a two-stage process. First, an AC-to-DC converter changes the alternating power to DC. Then, a DC-to-DC controller adjusts the voltage and current levels to the battery’s requirements.
Public fast chargers may receive higher voltage AC from the grid, and a similar conversion happens before the DC power enters the vehicle. However, using a DC charging station for charging does not require the help of an onboard converter; it only converts the current within the charging station. This ensures safe, efficient charging of the EV battery from any external power source.
New charging facilities have also proposed adding energy storage systems to help reduce grid pressure while providing stable and sustainable power sources. This new system reduces the impact of peak periods on the power of charging stations.
What is the Most Common EV Charger?
There is a growing need for convenient and best EV charging station options due to increased EV adoption. The three most prevalent types of chargers used worldwide include:
AC EV Charger
The AC charger for cars is by far the most common. The reason behind this is that it can tap into standard electrical wall outlets found in every home and business. It uses simple Level 1 or Level 2 charging and delivers electricity to the vehicle in the form of alternating current. Level 1 uses a basic 120V outlet, providing a range of about 5 miles per hour of charging. It requires no professional installation. Level 2 steps up to a 240V outlet for faster recharging. For example, an EVB Charger’s 7.4kW AC EV charger can add 40km of range per hour. Both allow unattended charging overnight.
AC chargers are relatively inexpensive, with Level 2 units costing $1200-2500 after installation.[1] For most everyday use cases, their lower power is not a significant limitation. As the cheapest and most widely available option, AC charging dominates the residential market.
DC EV Charger
Alternatively, direct current delivered via DC fast charger means filling a vehicle’s batteries in 30 minutes or less. DC chargers require a more powerful input current and converter technology to achieve these speeds.
DC fast chargers, located in public areas and along highway corridors, use specialized connectors like CHAdeMO and CCS. The best EV charging station units in this category have a higher cost in the range of $10,000-50,000 per charger but enable long-distance driving.[1] DC ones are mainly used for public charging stations or fleet depots where quick recharges are crucial.
Portable EV Charger
Compact portable chargers are a practical way to top up batteries from any standard 120V outlet for ultimate flexibility on the go. With a light design, portable chargers are affordable and easy to transport in a car or be placed in a backpack. A meters-long charging cable enhances its convenience, making it suitable for special scenarios such as narrow aisles and scenes without outdoor sockets.
While they deliver moderate charging speeds, portables provide peace of mind as an emergency backup or for charging away from home infrastructure when needed. Their lightweight and plug-and-play design makes them very convenient supplemental chargers.
Where Can I Charge an Electric Car?
EVs don’t just offer environmental and cost benefits; they are also easy to recharge virtually anywhere. This is one of the top factors in their growing popularity. EV owners have multiple convenient options:
EV Charging at Home
For many, the garage or driveway is where their electric vehicle spends its nights plugged into a dedicated home charger. With smart controls, home charging occurs while owners sleep. Installation of a Level 2 best EV charging station unit is simple and provides a full charge by morning. Having a reliable at-home charging setup allows daily commutes without worrying about range. Moreover, another benefit of purchasing a household charger is that car owners only need to pay the charging fee according to the household electricity price!
EV Charging at the Workplace
As more companies add one or several stations for employees, workplace EV charging has taken off as well. Plugging in for a few hours during the workday tops up batteries enough to handle evening plans. Some forward-thinking employers even convert company fleet vehicles to EVs with dedicated fast-charging depots. Having a station at the office eliminates “range anxiety” for many drivers.
Moreover, more and more companies hope to cultivate employee loyalty by improving this infrastructure. Supermarkets and retail stores can also attract potential customers through EV chargers.
EV Charging on the Road
Whether it’s stopping for groceries or taking a road trip, highway travel centers and shopping malls are embracing EV charging as a new amenity. Drivers only need minutes with a 150kW+ DC fast charger to gain hundreds of travel miles. Apps help locate and pay for these third-party stations so charging remains seamless away from home. The emerging public best EV charging station network is enabling true electric road trips. In addition, drivers can also achieve charging freedom on the journey through portable EV chargers.
By offering options to charge almost anywhere, the growing infrastructure makes driving electric vehicles truly more convenient than gasoline cars. Owners have freedom and flexibility provided by charging solutions at home, work, and across town or country.

How Long Does it Take to Charge an Electric Vehicle?
The short answer to this most common question is it varies based on two specific factors. These include the charger’s power level and the battery pack’s size.
Let’s take an example of a typical 60kWh EV battery. When this battery is charged via a 22kW Level 2 home charger, the charging process starts quickly but slows down as the battery nears full. For a full 100% charge from empty, it may take around 2h40min. It can be fully charged before you sleep.
If using a faster DC charger, times are significantly reduced. A 120kW best EV charging station takes approximately 25 minutes to go from 10-80% full, providing hundreds of miles of range replenished. The final top-up to 100% may add another 5 minutes. Moreover, if you use a 180kW EV charger, you only need to wait 20 minutes to charge your vehicle!
As batteries increase in size to provide longer ranges, charge times are also longer. For a 90kWh battery, the 22kW home charger would need around 4 hours for a 0-100% charge. However, a high-powered 180kW DC fast charger could attain 80% charge status in just 20-25 minutes, replenishing hundreds of miles of travel distance in under an hour. Similarly, if you use a 120kW EV charger, you just need 45 minutes to start the journey.
By utilizing faster charging infrastructure where available, EVs can receive charges similar to gasoline in refueling duration when longer stops are possible. Home charging overnight remains ideal for daily use, keeping batteries topped up.
How Much Does EV Charging Cost?
EV ownership offers long-term cost savings over gasoline thanks to lower charging and maintenance expenses. Many governments also provide generous incentives:
- The Netherlands reduced energy tax, saving up to €4.25/session with public charging. Installing an EV charger can save €470 per year now.
- Sweden provides lower annual vehicle taxes and reduced company car taxation. Families purchasing EV chargers can gain a 50% subsidy!
- France exempts full EVs from the CO2-based tax component. They also provide up to €5,000 in personal subsidies for EV owners.
- The UK offered up to 75% subsidy for home chargers. They exempt EVs from some annual taxes as well.
- Norway has very low annual EV road fees of just €48 and no purchase tax on affordable EVs. Larger incentives make ownership highly subsidized.[2]
Besides, if we take UK electricity prices of 29p per kWh as an example, using a home EV charger to fuel an electric vehicle with a 60kWh battery typically costs £17.4.[3] Using public charging stations will require corresponding additional charging fees. The travel cost of electric vehicles is low and is recommended without causing environmental pollution.
Furthermore, compared to fuel vehicles, the electric vehicle does require low maintenance costs and less maintenance frequency. These cost savings truly accumulate over the years of vehicle ownership. As EVs become more economically feasible to manufacture, these economic advantages are solely anticipated to amplify as time progresses.
How Can I Maintain an EV Charging Station?
Keeping the best EV charging station in optimal working condition requires regular upkeep over its lifetime of service. Proper maintenance ensures the charger continues powering electric vehicles safely and efficiently for every charging session to come. Here are some best practices to follow:
Follow the Guideline
Refer to the guide frequently and recommend others do as well. It outlines full details of exactly what procedures to follow for safety and longevity. Check for software/manual updates every 3 months on the manufacturer’s website. Confirm that any regional or vehicle-specific requirements are being met precisely. Consider signing up for maintenance reminder communications. Keep comprehensive service records, including hours used, error codes, repairs, and component replacements. This historical data helps technicians address potential problems.
Regular Inspection and Cleaning
Perform full mechanical and electrical inspection every use by visually and manually examining all external parts for signs of damage, abrasion, cracks, or discoloration, which could indicate environmental deterioration or internal failures developing. Twice annually, more thorough tear-down cleaning is conducted by professional personnel. Use an array of specialized tools to ensure the absolute removal of contaminants in all recessed areas and a protective, refreshed finish.
Avoid Overcharging
Check the state of the charge display, mobile app, or onboard vehicle charger screen when charging is complete. Occasionally verify against the battery percentage readout as well. Drivers are suggested to stop charging at around 80-90% capacity rather than waiting for 100% to keep the battery healthy for the long term. For fleets, consider integrating charge limits directly into vehicle settings.
Avoid Overheating or Use of Damaged Circuits
Pay close attention to ambient conditions, especially for outdoor units. Relocate the charger or improve ventilation by adding a small fan or extending vent ducting if temperatures rise into the excessively hot or cold ranges. Replacing worn or damaged parts promptly is needed due to safety and performance risks from things like exposed wiring.
Regular Maintenance
Rigorously follow the service schedule for calibration, testing, and inspections periodically. Also, consider extended maintenance plans providing multi-point health checks and part replacements annually, ensuring the charger can always run well. Keep one backup charger available if repairs are needed to minimize downtime disrupting routines. Proper upkeep is vital for equipment dependability and compliance with local codes.
Storage Precautions
Electric vehicle chargers have a wide storage temperature range, and specific values can be found on the manufacturer’s official website or by contacting sales personnel for specific information. Improper storage may have an impact on the performance of the charger. Furthermore, it is recommended not to place heavy objects on the charger to avoid deformation of the charger casing or damage to the internal structure.
Proactive maintenance and cleaning help keep your best EV charging station running optimally for many miles of electric driving. Following all the manufacturer’s guidelines maximizes the usable lifetime.
Who Makes the Best EV Charging Stations?
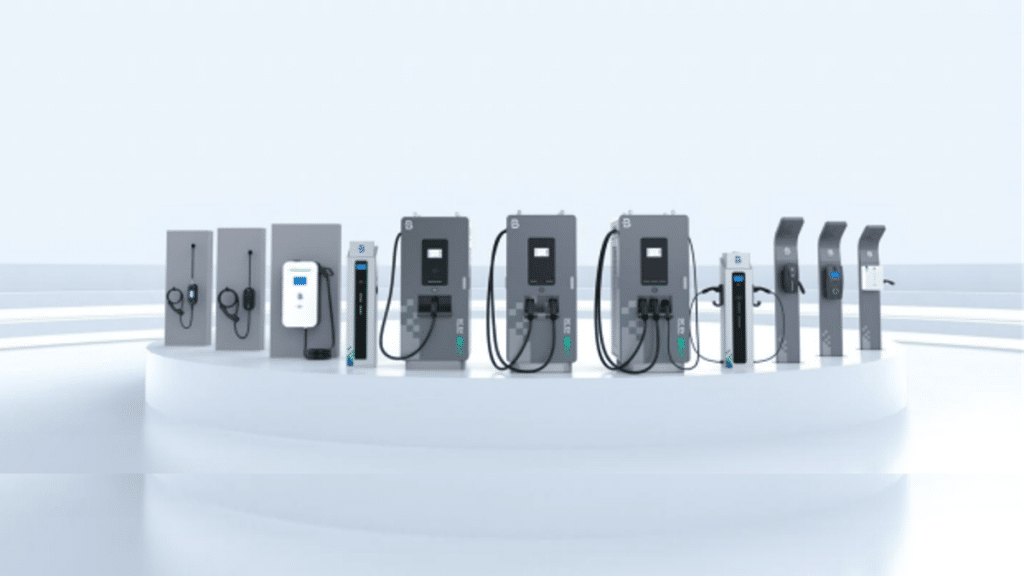
There are many reputed EV charging station suppliers in the market that offer quality products. An important thing to consider when it comes to ensuring you get the best EV charging station is to look for a brand that offers safety certifications and long industry experience. They help ensure the charger will perform safely and efficiently for years. EVB Charger satisfies all these criteria and offers much more.
The reputed brand EVB Charger, a subsidiary of BENY, is known for its power electronics expertise. Its UL, CE, and other qualifications are engineered for performance, efficiency, and safety. The company’s diverse AC and DC EV chargers meet every charging scenario need from homes, workplaces, and public stations. Relying on innovation, EVB Charger pushes boundaries to deliver pioneering solutions. As an advanced EV charger supplier, EVB Charger continuously accelerates widespread EV adoption. Some of its popular products include:
AC EV Charger with Socket
EVB Charger’s AC EV Charger with Socket is a sleek yet powerful residential charging solution. With its IP55/65 weatherproof housing and intelligent software control, it allows reliable charging anywhere outdoors or indoors. Its key features include:
- Sturdy wall mounting design for indoor or outdoor installation
- IP55/65 rating protects against water, dirt, and corrosion from rain, snow, dust, and sun
- 4-22kW wide charging power provides quick and hassle-free travel
- OCPP 1.6J protocol with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth facilitates remote monitoring and control via the smartphone app
- Set kWh meter to measure the energy used for EV charging
- Advanced safety features protect against over-voltage, under-voltage, over-temperature, and more
- Generous 24/7 customer support by phone and online
- About 100% efficiency

Floor-Mounted 3 Guns DC EV Charger
For high-speed public charging, this best EV charging station takes performance to new levels. Its floor-standing cabinet contains up to three independent chargers capable of filling batteries within minutes. Its features include the following:
- Rugged floor-standing cabinet with a stylish design for deployment anywhere
- Modular design allows for 1, 2, or 3 independent charging stalls of 82kW-262kW power each
- 3 guns with CCS1 and CCS2, CHAdeMO, and AC (optional) connectors for widespread EV compatibility
- Super-fast charging. The unit can provide a 74km distance with just 10 minutes charge at 82kW and more with higher charge configurations
- 1-inch bright LCD plus LED indicators clearly communicate stall status
- 4G cellular modem and OCPP 1.6 protocol enable remote monitoring, control, and firmware updates
- IP55-rated enclosure withstands weather at corridors and depots
- Touchscreen interface simplifies attendants’ and drivers’ experience
- Advanced safety features and protections against over-voltage, under-voltage, over-temperature, etc. to ensure maximum reliability
- CE and RoHS certified to meet international standards for safety and performance

Portable + Wall-mounted 2 in 1
This best EV charging station leads the way as the ultimate in flexible charging. One compact unit functions as both a portable and wall-mounted charger, seamlessly switching between 7.4kW and 22kW outputs. The key features that make it an attractive choice include:
- Converts seamlessly between portable and wall-mounted modes within minutes
- Compact size and design allow the charger to be carried easily anywhere needed
- Wall-mount bracket stores discreetly on the rear for permanent installation
- Includes multiple types of connectors for wide flexibility and connectivity
- Lightweight design for effortless one-person transportability
- 3-inch display’s touch and swipe interface are optimized for use in any orientation
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity enables remote monitoring, scheduling, and electric vehicle service apps
- IP65 fully sealed housing withstands rain and dust
- Operate from -30℃ to 50℃
- Multiple safety features for fault detection, overcurrent protection, and more
- CE and RoHS-certified products for reliability and peace of mind
- Standard 7 meters of total length (customizable)
Conclusion
Overall, the expanded use of electric vehicles will rely heavily on convenient, affordable, and reliable public charging infrastructure. This guide has outlined the types of EV chargers available, where charging can occur, factors that affect charge times, cost considerations, proper maintenance practices, and what to look for in the best EV charging station manufacturer.
Choosing a brand like EVB Charger that has decades of experience and safety certifications, along with diverse, versatile product options, will help ensure smooth electric driving for years to come. Don’t miss the opportunity to meet your EV charging needs – visit EVB Charger’s official website today!
References
[1] How Much Does It Cost To Install An EV Charger? Available at: https://www.jdpower.com/cars/shopping-guides/how-much-does-it-cost-to-install-an-ev-charger (Accessed: 23 January 2024)
[2] Europe Road Incentives and Legislation. Available at: https://alternative-fuels-observatory.ec.europa.eu/transport-mode/road (Accessed: 23 January 2024)
[3] Current Price of Electricity Per kWh in the UK (2024) Available at: https://energyguide.org.uk/average-cost-electricity-kwh-uk/ (Accessed: 23 January 2024)

