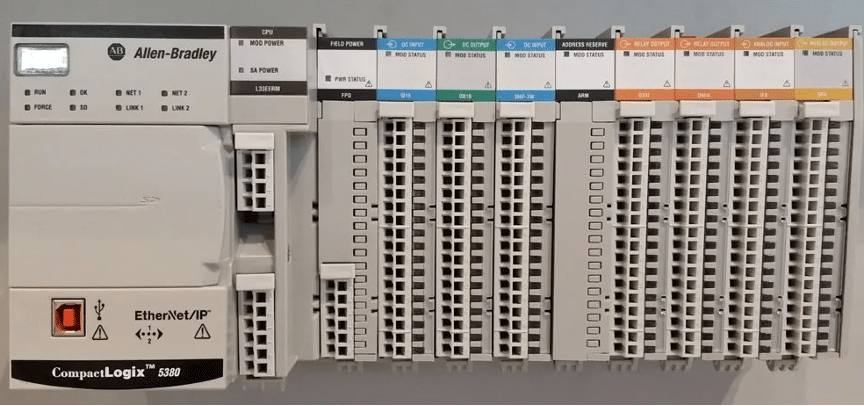
PLC controller, also known as a Programmable Logic Controller, is an electronic device widely used in the field of industrial automation control. The operational logic of PLC controllers is controlled by pre-programmed code. It is a digital control system that, based on predefined programs and the detection and processing of input signals, performs logical operations to control output devices. PLC controllers find extensive applications in various industrial sectors, including transportation, manufacturing, energy, and smart homes. They are required to be installed in specific control cabinets, and these cabinets need proper temperature dissipation to prevent the controller from overheating and to enhance its lifespan. PLC controllers are known for their stability, high reliability, and strong scalability, making them suitable for controlling various devices and systems such as automated production lines, metallurgy, machinery, light industry, chemical, and textile industries.
Basic Components of PLC Controllers
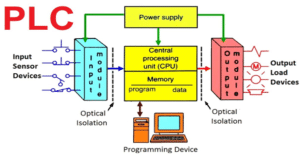
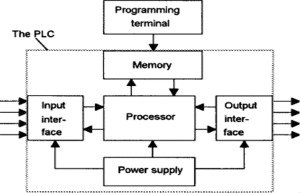
PLC controllers consist of three fundamental components: input modules, output modules, and a central processor.
- Input Modules: These modules receive signals from external devices, convert them into digital signals, and monitor various signals in real-time during program execution. Examples include signals from sensors, which are converted into digital signals by input modules and then processed by the central processor.
- Central Processor: The core of the PLC, comprising a CPU chip and memory. The CPU continuously collects input signals, executes pre-written programs for monitoring and computation, while the memory stores programs and data, providing storage space to ensure orderly program execution.
- Output Modules: These modules transform information and signals computed by the central processor into control signals that field-executing components can receive. Examples include control signals for solenoid valves, light displays, motors, and other executing mechanisms.
Operation Principles of PLC Controllers
The working principle of PLC controllers involves running programs stored in the PLC to control devices. The process typically comprises three stages: input sampling, user program execution, and output refreshing. These stages collectively form a scanning cycle, and the PLC repeats these stages throughout its operation.
Functions of PLC Controllers
- Safety, Stability, and Reliability: PLC controllers, constructed with high-quality electronic components, operate safely and reliably in complex industrial environments.
- Efficient Automation Control: PLC allows the coding of programs to automate entire processes, reducing manual labor costs and improving production efficiency.
- Convenient Post-Maintenance: The modular design of PLC facilitates post-maintenance. Faulty modules can be replaced directly, ensuring quick and convenient maintenance.
- Wide Applicability: The program ability of PLC makes it highly flexible and convenient in practical applications. Once a corresponding code program is written to meet specific requirements, it can broadly satisfy various production needs, enhancing its versatility.