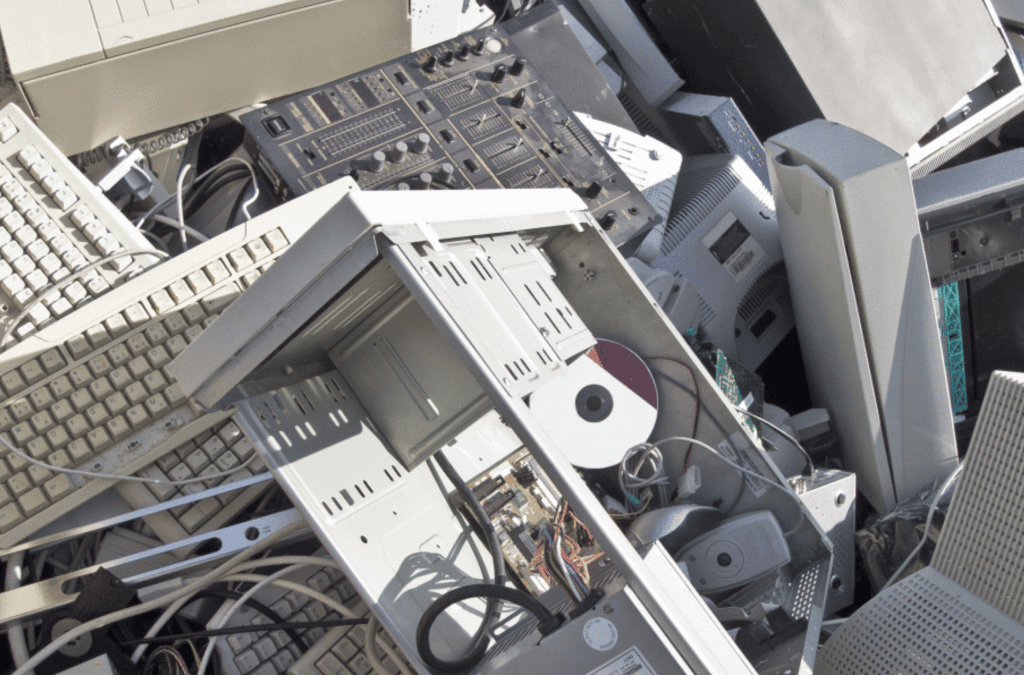
eWaste is an increasing problem worldwide, and it’s not just because of a global desire for new gadgets. As more people are using technology, the world is seeing an increase in the amount of eWaste that fills our landfills. But what is eWaste, and how does it affect us?
What is eWaste?
eWaste is the term used to refer to discarded electrical and electronic devices. Today, with the advancement of technology, there are many different devices that are considered eWaste: laptops, smartphones, TVs, lamps, and even items like fridges and solar panels.
Impact of eWaste
eWaste has become a prevalent issue because it is piling up in our landfills. Modern electronics are safe to use, but most of them contain materials like gold, silver, copper, and Palladium; these are valuable materials that can be harvested from electronic devices and reused, but unfortunately, only about 20% of the world’s electronic devices are properly recycled.
The rest of the eWaste ends up in landfills or incinerated, where it can have different impacts.
Air Pollution
When eWaste is incinerated, the metals and other materials Within can release particles, which can travel in the air for miles. This can affect people in nearby towns and cause respiratory issues.
Additionally, when we mine for the metal that is in e-waste, we are releasing carbon emissions from the Earth. If we were to recycle the metal from the eWaste instead of incinerating it, there would be less of a need for mining.
Soil Contamination
The metals and materials from e-waste seep into the ground in landfills as the devices break down, poisoning the soil. This contamination can kill the microorganisms living in the dirt.
Water Contamination
The metals and other hazardous materials that have leached into the soil from e-waste continue down into the Earth until they reach groundwater, where they can then travel to waterways into other bodies of water. Not only do the metals and materials raise the acidic levels of the bodies of water, but their presence can disturb entire ecosystems.
Identity Theft
There are a surprising amount of people who do not clear the information from their electronic devices before they throw them out, which leaves them susceptible to identity theft.
How to Prevent eWaste
Together, we can reduce the amount of eWaste that ends up in landfills and is incinerated by both reusing and recycling electronic devices.
When devices are broken beyond repair, there are collection centers where you can recycle them at. Some towns even have electronic collection days, where you can leave them out on your curb.
You can reuse your electronic devices by purchasing used and selling your used electronics online. The odds of finding a used model of the item you’re looking for are high; gently used models are just as good as new models, and they cost less.
There are ways to prevent the harmful effects of eWaste, and there are things you can do to start doing your part today.