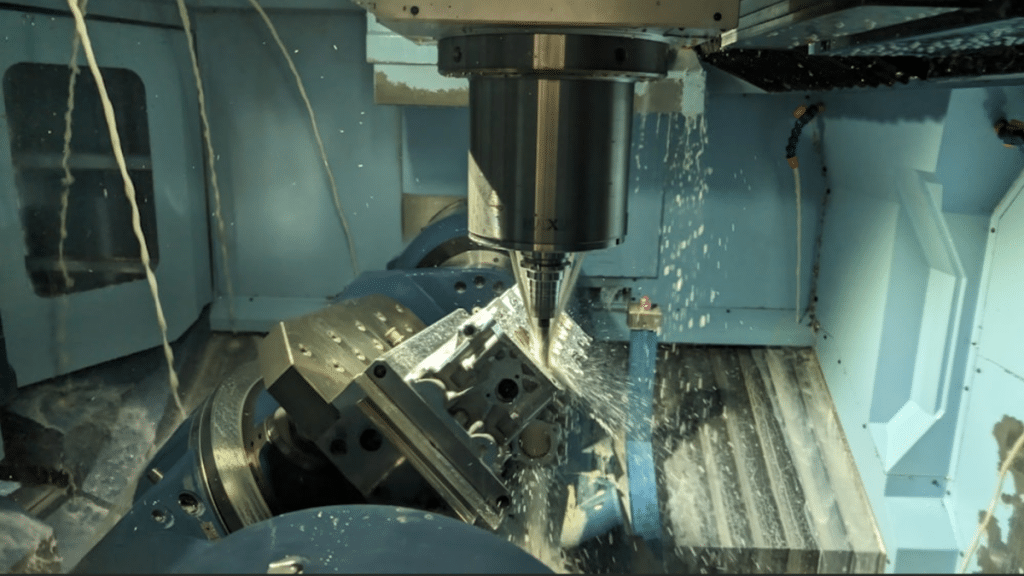
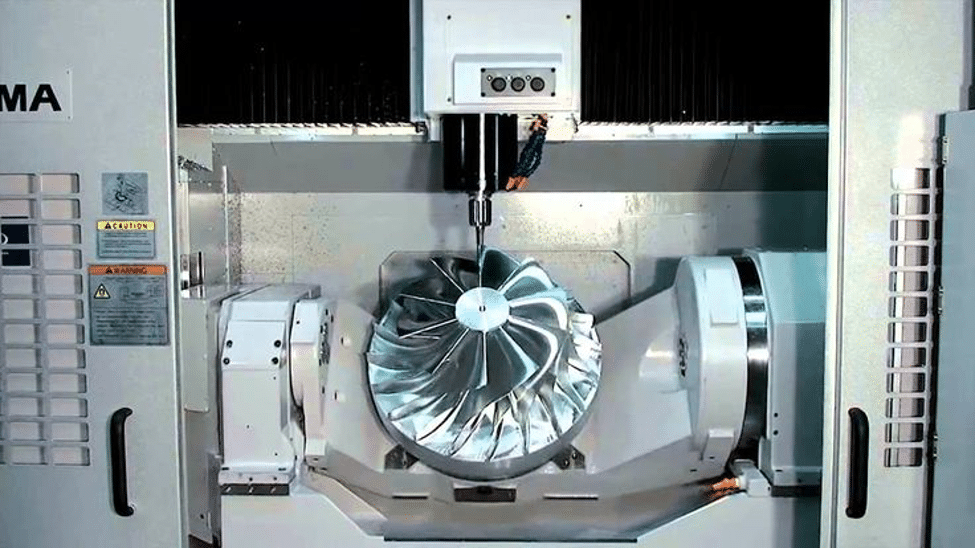
CNC machining is hugely important in modern society for making complicated pieces in lots of fields. By computerizing how things are made, it automates most of the cutting and molding of pieces. Therefore, it increases precision, accuracy, and consistency when creating stuff. There’s mainly 3-axis CNC machining and 5-axis machining. Both use computer number control to subtract material from an initial block. However, they differ in the degree of freedom of movement possible during the process.
3-axis and 5-axis CNC Machining: Overview, Working Principles, and Pros and Cons
3-axis CNC machining involves movement along three linear axes – X, Y, and Z. The cutting tool translates along these axes to mill or cut parts from raw stock. It works on the principle of programming paths for the tool to follow along the three axes as it removes material layer by layer. Its pros and cons include:
- Pros: Simple design keeps machining costs low. Setup and programming are easier for basic shapes when compared to 5-axis machining.
- Cons: Limited to planar surfaces, so complex contouring or internal features are difficult to machine.
5-axis machining adds rotational movements around two additional axes – the A and B axes. This allows the positioning of the cutting tool at various angles relative to the workpiece. It works on the principle of incorporating five degrees of freedom for automated multi-axis movements during machining. Its pros and cons include:
- Pros: Can access hard-to-reach internal areas and undercuts. Complex contours and sculpted shapes present no difficulty.
- Cons: Much more complex kinematic design increases machining costs. Programming and operating five-axis machines require advanced expertise and is more time-consuming than 3-axis CNC machining.
3-axis Vs. 5-axis CNC Machining Center
3-axis CNC machining and 5-axis machining are compared on complexity, cost-effectiveness, efficiency, and machining capability.
1. Complexity
With only three linear axes, 3-axis machines have a simpler mechanical design that makes them more cost-effective and reliable than 5-axis milling machine systems. However, they offer limited rotational capabilities. 5-axis systems incorporate two extra rotary axes, making their designs far more intricate.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
The initial investment required for a 3-axis machine is much lower than for a 5-axis machine of comparable volume. This is because 3-axis machines have a simpler mechanical design. However, the tradeoff is that 3-axis CNC precision machining struggles to produce parts with undercuts or complex contouring. By facilitating complex parts in a single setup, 5-axis machining improves cost-efficiency despite its higher purchase cost.
3. Efficiency
For basic prismatic components, 3-axis machines complete jobs more swiftly. But complex sculpted components usually require repeat fixturing on 3-axis CNC machining to machine all surfaces, decreasing efficiency. 5-axis machining optimizes tool access, enabling full machining in one clamp. There’s precise gouging even in confined areas. Hence, it vastly improves process efficiency overall.
4. Machining Capability
While the 3-axis can only cut planar or straight-walled features, the 5-axis comprehensive rotational ability permits even interior geometries. These can be machined without mechanical obstructions. 5-axis machining offers unrestrained cutting across multiple non-parallel surfaces in a single clamp.

Applications Cases of 3-axis and 5-axis CNC Precision Machining
Both 3-axis CNC machining and 5-axis machining are widely used across industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, etc. However, there are some key differences.
1. Automotive
3-axis mills body panels, brackets, and other structural components where flat surfaces predominate. However, for injection tooling like molds and dies producing undercut designs, 5-axis machining truly comes into its own. It enables the complete sculpting of interior contours efficiently.
2. Aerospace
Planar airframe panels are adeptly cut via 3-axis CNC machining for wing and fuselage production. Meanwhile, the 5-axis plays a vital role in gas turbine development. Intricate impeller forms with precise internal cooling paths are out of reach for anything but multi-axis control.
3. Medical
Simple cutting of prosthetic sockets or dental copings leverages the programming simplicity of 3-axis CNC machining. But within live surgical tooling and intricate bone implants, the 5-axis CNC machining center shines. It allows anatomical curvature to match effectively.
MY Prototyping Offers Custom CNC Machining Services
MY Prototyping is a professional one-stop solution provider integrating design, low-volume production, mass manufacturing, finishing, and assembly services. The brand prides itself on being focused on end users’ needs. Its custom CNC machining services provide customizable CNC machining tailored for engineers and designers’ prototyping and low-volume production needs. The top features that make them preferable include:
- Precise Tolerances: Parts machined within 0.01mm tolerances
- Quick Turnaround: Quality CNC parts in as fast as 3 working days
- Diverse Materials: Machining over 40 material types
- Online Quoting: Instant quotes for competitive pricing
- ISO Quality: Proven processes meeting ISO 9001:2015 standards
Conclusion
Overall, 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machining offer solutions for manufacturing a variety of complex parts routinely seen across industries. While the 3-axis handles simple parts well, the 5-axis permits multi-surface components. The custom CNC manufacturing services provided by MY Prototyping deliver precision and quality from prototype to mass production runs. Visit the company’s website to explore how its expertise in CNC machining can help transform your product from design to reality.